

Targeted Harassment: The Ukraine Whistleblower
Overview
In the fall of 2019, a whistleblower logged a complaint about President Trump’s dealings with Ukraine. A coalition of conservative and right-wing influencers and conspiracists encouraged campaign participants to keyword squat the name of an individual who they alleged was the whistleblower. Mainstream press outlets implemented a media blackout to protect the identity of the whistleblower, which involved never printing the name of anyone alleged to be the person, including the target of the keyword-squatting campaign. After attribution to this spread, some social media platforms blocked the use of his name. This asymmetrical media environment shaped the breaking news event and led to misidentification and targeted harassment.
(NOTE: In order to compile this case study accurately without furthering the aims of the manipulation campaign it details, we will refer to the targeted individual as “C” in this text wherever possible. The name will only be used in direct quotes, screenshots, or footnotes, per the URLs and headlines of articles being cited.)
STAGE 1: Manipulation Campaign Planning and Origins
On August 12, 2019, an anonymous government whistleblower filed a complaint to the US Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, asserting that President Trump had engaged in illegal discussions with Ukraine over Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden. This disclosure entered public conversation on September 19 when The Washington Post released an article about the whistleblower complaint.1 On September 23, the committee released a redacted version of the complaint,2 which eventually led to an investigation and ultimately the impeachment of President Trump on December 18.3 As the Ukraine scandal captured national attention, a loosely affiliated online networked faction swarmed to unmask the whistleblower. Federal whistleblowers are protected by law from retaliation by the government, which can include protecting their anonymity.4
On social media, users, particularly political opponents of Joe Biden on the right, engaged in wide-scale speculation about the whistleblower’s identity. Some users of 4chan’s Politically Incorrect board began investigating the from The Washington Post, with explicit plans to seed their expected findings on social media.5 These investigations resulted in several false leads and misidentifications, including a September 30 4chan thread claiming Democratic National Committee contractor Alexandra Chalupa was the whistleblower.6
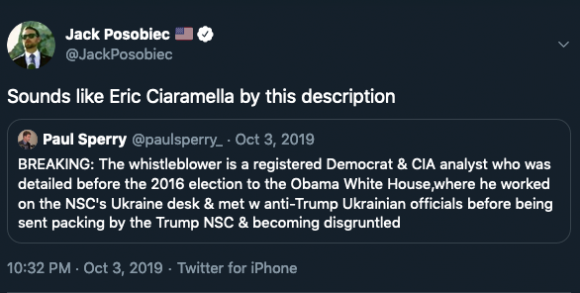
On October 3, conspiracist and activist Jack Posobiec first speculated in a retweet that CIA analyst "C" may match a leaked description of the whistleblower.7 He posted another speculative tweet about "C."8 Some participants in this breaking news conversation on Twitter referenced a (now republished) Medium post written by Mike Cernovich from 2017, in which Cernovich accused "C" of being “the main force pushing Trump-Russia conspiracy theories.”9
- 1Ellen Nakashima et al., “Whistleblower Complaint about President Trump Involves Ukraine, According to Two People Familiar with the Matter,” The Washington Post, September 19, 2019, sec. National Security, https://www.washingtonpost.com/national-security/whistleblower-complaint-about-president-trump-involves-ukraine-according-to-two-people-familiar-with-the-matter/2019/09/19/07e33f0a-daf6-11e9-bfb1-849887369476_story.html.
- 2 “House Intelligence Committee Releases Whistleblower Complaint,” U.S. House of Representatives Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence, September 26, 2019, https://intelligence.house.gov/news/documentsingle.aspx?DocumentID=708.
- 3Nicholas Fandos and Michael D. Shear, “Trump Impeached for Abuse of Power and Obstruction of Congress,” The New York Times, December 18, 2019, sec. Politics, https://www.nytimes.com/2019/12/18/us/politics/trump-impeached.html
- 4Eugene Kiely, “Legal Implications of Outing the Whistleblower,” FactCheck.Org (blog), November 20, 2019, https://www.factcheck.org/2019/11/legal-implications-of-outing-the-whistleblower/.
- 5Anonymous, “/pol/ - Politically Incorrect » Thread #227960432,” , September 27, 2019, accessed via 4plebs, https://archive.4plebs.org/pol/thread/227960432/#227962012.
- 6Anonymous, “/pol/ - Politically Incorrect » Thread #228373219,” 4chan, September 30, 2019, accessed via 4plebs, https://archive.4plebs.org/pol/thread/228373219/#228373219.
- 7Jack Posobiec (@JackPosobiec), "Sounds like Eric Ciaramella by this description," , October 3, 2019, https://twitter.com/JackPosobiec/status/1179947453803646977.
- 8Jack Posobiec (@JackPosobiec), "I wonder what Eric Ciaramella is up to these days," Twitter, October 3, 2019, https://twitter.com/JackPosobiec/status/1179972767686578176.
- 9 Mike Cernovich, “2017 Cernovich Article – Meet Eric Ciaramella — H.R. McMaster Appoints Susan Rice Ally to Be His Personal Aide,” Mike Cernovich (blog), November 17, 2019, https://www.cernovich.com/2017-cernovich-article-meet-eric-ciaramella-h-r-mcmaster-appoints-susan-rice-ally-to-be-his-personal-aide/.
STAGE 2: Seeding Campaign Across Social Platforms and Web
The seeding process of the campaign to spread the allegation that “C” was the whistleblower involved the strategic release of documents alleged to support the claim by operators on Twitter. On October 11, writer Seamus Bruner tweeted the image of a document supposedly detailing "C’s” role in US-Ukrainian diplomatic relations.1 The claim was reiterated first in a tweet by writer Greg Rubini on October 11,2 and then in a follow-up thread on October 15.3
On October 30, these initial claims were traded up the chain into more legitimate circles when Real Clear Investigations released a report identifying "C" as the whistleblower, without direct reference to Jack Posobiec who initially popularized the claim on Twitter.4 Political provocateur Dinesh D’Souza further amplified the claim in a retweet of an article from The Hill on October 31.5 Also on October 31, following the Real Clear Investigations report, Rush Limbaugh named "C" on his radio show.6
The claim that "C" was the whistleblower spread over the subsequent week, resulting in 150,000 tweets naming him.7 During this time, North Carolina businessman Tim D’Annunzio reportedly used Facebook ads to spread the name, specifically microtargeting Christians.8
On November 6, political columnist Benny Johnson shared an image of a transcript of the closed-door congressional impeachment testimony of William Taylor, the former acting ambassador to Ukraine. The document had reportedly been released on the House of Representatives Committee Repository website that day, though the testimony occurred a month prior, and it showed the GOP’s lawyer asking Taylor directly about "C’s" name. The document is no longer on the committee website, but remains live and unredacted on NBC.9 That same day, Donald Trump Jr. tweeted a link to a Breitbart article about "C," writing “Because of course he did!!! Alleged ‘Whistleblower’ Eric Ciaramella Worked Closely with Anti-Trump Dossier Hoaxer.”10
On November 7, a prominent Qanon-associated Twitter user “Eyes on Q” shared a collage of recontextualized images of Alexander Soros, the son of billionaire investor and philanthropist George Soros, with a variety of Democratic leaders. While this account did not identify Alexander Soros as the whistleblower, the image was subsequently shared on and reposted on fringe news site The Buffalo Chronicle on November 10.11 Both young white men with short beards, Soros and "C" share some visual similarities, which led some campaign participants to misidentify Soros as "C," and share that misidentification across the web.12 Soros wasn’t the only one. Other men whose photos were misidentified as that of "C" include former Obama administration official David Edelman, French presidential advisor Hugo Verges, and Ukranian Rostyslav Pavlenko.13
While some press and reporting contributed to the spread of the whistleblower’s alleged identity and image, the conversation was driven by . “Please do not retweet this photo of the scam-whistleblower,” Candace Owens tweeted on November 8, followed by a hashtag of his full name, and the claim, “He does not want his name or picture to go viral so please, whatever you do, do not hit the retweet button. Thank you in advance.”14 From November and onward, other campaign participants continually seeded "C’s" name on small blogs, Twitter, Facebook, , Gab, YouTube.15 The asymmetrical media environment, in which the right freely used "C's" name while the left did not, allowed campaign participants to add noise around who the whistleblower was, and if he had been positively and officially identified.
- 1 Seamus Bruner (@seamusbruner), “If it turns out Eric Ciaramella is Schiff’s informant, people ought to know that Billionaire Clinton donor Victor Pinchuk sent 🇺🇦 MP Bielkova to meet with him same day she met with David Kramer and kicked Steele Dossier operation into high gear. ie “Whistleblower” = Dossier 2.0,” Twitter, October 11, 2019, https://twitter.com/seamusbruner/status/1182714514585903105.
- 2Greg Rubini (@GregRubini), "we know WHO is the 'WHISTLEBLOWER' Eric Ciaramella Eric Ciaramella is an obama HOLDOVER at the NCS, inside the White House." Twitter, October 11, 2019, https://twitter.com/GregRubini/status/1182649700660531201.
- 3 Greg Rubini (@GregRubini), "1. imagine if at a dinner in Washington DC, in Oct 2016, you had: - John Brennan, Director of the CIA - Susan Rice, Obama's Nat. Security Adviser together with Eric Ciaramella - the Adam Schiff 'whistleblower'... [THREAD] please retweet.," Twitter, October 15, 2019, https://twitter.com/GregRubini/status/1184073487901704192.
- 4Paul Sperry, “The Beltway’s ‘Whistleblower’ Furor Obsesses Over One Name,” Real Clear Investigation, October 30, 2019, https://www.realclearinvestigations.com/articles/2019/10/30/whistleblower_exposed_close_to_biden_brennan_dnc_oppo_researcher_120996.html.
- 5Dinesh D’Souza (@DineshDSouza), "Eric Ciaramella worked for John Brennan. He has close ties to Biden. He’s a Deep State hit man. No wonder Pelosi doesn’t want us to publicize the guy’s name and background," Twitter, October 31, 2019, https://twitter.com/DineshDSouza/status/1189918034988818433.
- 6Ellie Bufkin, “Rush Limbaugh: Alleged Whistleblower ‘Looks like the Pajama Boy in the Obama Ad,’” The Washington Examiner, November 1, 2019, https://www.washingtonexaminer.com/news/rush-limbaugh-alleged-whistleblower-looks-like-the-pajama-boy-in-the-obama-ad.
- 7Isaac Stanley-Becker and Craig Timberg, “Trump’s Allies Turned to Online Campaign in Quest to Unmask Ukraine Whistleblower,” The Washington Post, November 7, 2019, https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2019/11/07/trumps-allies-turned-online-campaign-quest-unmask-ukraine-whistleblower/.
- 8Stanley-Becker and Craig Timberg.
- 9Benny (@bennyjohnson), “Um - why is Eric Ciaramella's name in the congressional Impeachment testimony? Dems said they would redact the name of the "whistleblower." 2 explanations: 1. Ciaramella is not the whistleblower 2. Dems messed up BIG TIME & printed the name of the leaker in their own document,” Twitter, November 6, 2019, https://twitter.com/bennyjohnson/status/1192224325086015488; NBC News, “Read the Full Transcript of Top Diplomat Bill Taylor’s Impeachment Testimony,” NBC News, November 6, 2019, https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/trump-impeachment-inquiry/read-full-transcript-top-diplomat-bill-taylor-s-impeachment-testimony-n1077676.
- 10Donald Trump Jr. (@DonaldJTrumpJr), "Because of course he did!!! Alleged ‘Whistleblower’ Eric Ciaramella Worked Closely with Anti-Trump Dossier Hoaxer," Twitter, November 6, 2019, https://twitter.com/DonaldJTrumpJr/status/1192078857031036931.
- 11Alex Kaplan, “How a Total Fabrication Connecting George Soros’ Son to the Whistleblower Went from the Underbelly of the Internet to Rep. Steve King,” Media Matters for America, November 15, 2019, https://www.mediamatters.org/twitter/how-total-fabrication-connecting-george-soros-son-whistleblower-went-underbelly-internet.
- 12Charlie Nash, “Steve King Falsely Claims Alexander Soros Is Whistleblower,” Mediaite, November 14, 2019, https://www.mediaite.com/politics/steve-king-goes-full-steve-king-posts-photos-of-george-soros-son-falsely-claiming-hes-whistleblower/.
- 13“Eric Leaks,” The Illustrated Primer (blog), January 4, 2020, https://apelbaum.wordpress.com/2020/01/04/eric-leaks/.
- 14Candace Owens (@RealCandaceO), "Please do not retweet this photo of the scam-whistleblower, #EricCiaramella. He does not want his name or picture to go viral so please, whatever you do, do not hit the retweet button.Thank you in advance.," Twitter, November 8, 2019, https://twitter.com/RealCandaceO/status/1192817302422601730.
- 15Paul Sperry, “The Beltway’s ‘Whistleblower’ Furor Obsesses Over One Name,” Real Clear Investigations, October 30, 2019, https://www.realclearinvestigations.com/articles/2019/10/30/whistleblower_exposed_close_to_biden_brennan_dnc_oppo_researcher_120996.html.
STAGE 3: Responses by Industry, Activists, Politicians, and Journalists
Politicians adopted the campaign, joining the quest to unmask the whistleblower, making the issue the subject of much partisan conflict in Senate committees.1 In a retweet of his official campaign account, @TrumpWarRoom, President Trump shared a The Washington Examiner article naming "C."2 On December 27, President Trump retweeted Twitter user @surfermom77, who explicitly called "C" the whistleblower.3
On November 14, Sen. Rand Paul called for the whistleblower to testify in the Senate impeachment hearings.4 On November 19, Rep. Steve King shared the aforementioned Alexander Soros misidentification collage, commenting, “Adam Schiff said, I do not know the identity of the whistleblower. @RepAdamSchiff here are four strong clues.”5 On December 11, Rep. Louie Gohmert named "C" in a House Judiciary Committee meeting,6 as did Paul in speech to the Senate on February 4, 2020.7 This resulted in a slew of media exposure.
There was a stark divide between how the right-wing press and liberal and mainstream press covered this breaking event in late October and early November, 2019. Some right-wing outlets like Breitbart News,8 The Gateway Pundit,9 Red State,10 and The Washington Examiner, among others, decided to include the name of the suspected whistleblower in their reporting. While the Daily Caller initially did not print "C’s" name in articles, he was named on the site’s on October 31.11 Other conservative publications like The Federalist12 and Fox News13 did not include his name in publication. Two Fox News guests did, however, name "C" live on air on November 7 and 11.14 Even in debunks of the Alexander Soros misidentification collage, right wing pundits like Mark Dice included "C’s" name.15
While liberal and mainstream press continued to cover the investigation, they universally refrained from naming "C." The choice to identify the suspected whistleblower was widely condemned by Democratic politicians and most press.
This absence of "C’s" name in mainstream press contributed to a data void, in which only unverified sources and some right wing press outlets dominated queries for the name on search engines. As a result of this asymmetry, it remains easy to find articles in right-wing press that allege "C" is the whistleblower, and nearly impossible to find any naming him as even a person of potential interest in mainstream or liberal media.
- 1Manu Raju et al., “Shouting Match Erupts in Vindman Deposition as Democrats Accuse Republicans of Trying to out Whistleblower,” CNN, October 29, 2019, https://www.cnn.com/2019/10/29/politics/vindman-testimony-whistleblower-identity/index.html.
- 2Ryan Broderick, “Right-Wing Publishers Have Found A Way To Post The Supposed Trump Whistleblower’s Name To Facebook,” BuzzFeed News, December 27, 2019, https://www.buzzfeednews.com/article/ryanhatesthis/trump-whistleblower-name-facebook.
- 3Colby Itkowitz, “Trump Shares Post with Alleged Whistleblower’s Name to 68 Million Followers,” The Independent, December 29, 2019, https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/us-politics/trump-twitter-impeachment-whistleblower-deleted-tweets-a9263396.html.
- 4 RCP Video, “Rand Paul: Eric Ciaramella Is A Material Witness And Must Testify,” November 13, 2019, https://www.realclearpolitics.com/video/2019/11/13/rand_paul_ukraine_whistleblower_is_a_material_witness_and_must_testify.html.
- 5 Derek Willis, “Deleted Tweet from Steve King,” ProPublica, November 14, 2019, https://projects.propublica.org/politwoops/tweet/1194983687508676609.
- 6Dareh Gregorian and Dartunorro Clark, “GOP Rep. Gohmert Publicly Names Person Some Republicans Say Is Whistleblower,” NBC News, December 11, 2019, https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/trump-impeachment-inquiry/gop-rep-gohmert-publicly-names-person-some-republicans-say-whistleblower-n1100281.
- 7David Morgan, “Republican Rand Paul Names Purported ‘whistleblower’ in the Senate," Reuters, February 4, 2020, https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-trump-impeachment-paul/republican-rand-paul-names-purported-whistleblower-in-the-senate-idUSKBN1ZY2FP.
- 8Aaron Klein, “Alleged ‘Whistleblower’ Eric Ciaramella Worked Closely with Anti-Trump Dossier Hoaxer,” Breitbart, November 6, 2019, https://www.breitbart.com/politics/2019/11/06/alleged-whistleblower-eric-ciaramella-worked-closely-with-anti-trump-dossier-hoaxers/.
- 9Jim Hoft, “Oops! ADAM SCHIFF Accidentally Leaks Name of Anti-Trump 'Whistleblower" Eric Ciaramella in Bill Taylor’s Transcript!,” The Gateway Pundit (blog), November 7, 2019, https://www.thegatewaypundit.com/2019/11/oops-adam-schiff-accidentally-leaks-name-of-anti-trump-whistleblower-eric-ciaramella-in-bill-taylors-transcript/.
- 10Elizabeth Vaughn, “Suddenly, Coincidences Involving the Whistleblower Abound,” RedState, November 2, 2019, https://www.redstate.com/elizabeth-vaughn/2019/11/02/suddenly-coincidences-involving-whistleblower-abound/.
- 11 Derek Hunter, “Whistleblower’s Cover Blown” The Daily Caller, October 31, 2019, https://dailycaller.com/2019/10/31/whistleblower-name-democrats-joe-biden/.
- 12Margot Cleveland, “SCOOP: CIA, FBI Informant Was WaPo Source For Russiagate Smears,” The Federalist, November 4, 2019, https://thefederalist.com/2019/11/04/scoop-cia-fbi-informant-was-washington-post-source-for-russiagate-smears/.
- 13Oliver Darcy and Brian Stelter, “Fox News Executives to Network Hosts and Personalities: Do Not Identify the Whistleblower,” CNN, November 6, 2019, https://www.cnn.com/2019/11/06/media/fox-news-whistleblower/index.html.
- 14Jeremy Barr, “Fox News Guest Names Suspected Ukraine Whistleblower,” The Hollywood Reporter, November 7, 2019, https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/news/fox-news-guest-names-suspected-ukraine-whistleblower-1253260; Joey DePaolo, “Fox News’ Mollie Hemingway Names Whistleblower On Air,” Mediaite, November 11, 2019, https://www.mediaite.com/tv/watch-the-stunned-reaction-of-fox-news-howard-kurtz-after-a-fox-news-contributor-names-the-whistleblower/.
- 15Mark Dice (@MarkDice), "For the 1000th time, this is NOT Eric Ciaramella, the 'whistleblower.' This is George Soros' son, Alexander Soros. Stop spreading fake news.," Twitter, January 30, 2020, https://twitter.com/MarkDice/status/1223007386442420224.
On November 19, Republican congressman Steve King shared an Alexander Soros misidentification collage, commenting, “Adam Schiff [Democratic congressman] said, I do not know the identity of the whistleblower. @RepAdamSchiff here are four strong clues.” Credit: Screenshot by @IAStartingLine on Twitter.
STAGE 4: efforts
While most major proactively implemented editorial bans on “C’s” name being mentioned as soon as the campaign to unmask the whistleblower settled on “C” as the suspect of interest and took off, social media platforms intervened reactively and asynchronously. On November 8, Facebook announced that it would be removing mentions of “C’s” name from its platform and , while Twitter took a different approach, allowing the use of the name so long as there was no further identifying information that could lead to . Twitter did, however, prevent his name from trending, de-indexing it, despite allowing use of the hashtag.1 On February 13, YouTube removed a video of Rand Paul stating that “C” was the whistleblower in a speech on the Senate floor,2 and subsequent content with “C’s” name in the title.3 Reddit took no mitigation efforts to suppress the name.4 Wikipedia editors reportedly prevented “C” being named as the whistleblower.5 “C” does not have a dedicated Wikipedia page, and his name is not mentioned in the Trump-Ukraine scandal entry.6 All major search engines, like and Bing, did not intervene in hiding or redirecting search results for “C’s” name.
In addition to the by mainstream press, the work of the Alexander Soros misidentification was done by groups like Media Matters,7 AP,8 and FactCheck.org,9 all of whom refrained from identifying "C" in their reporting.
STAGE 5: Adjustments by campaign operators
As “C” has a relatively unique name, and as no mitigation efforts to disrupt web search results were put in place, that chose to allow the name to be published populate search engines. Despite mitigation efforts from some social media platforms like Facebook, campaign participants adapted tactics. They took to sharing links, , and images, and modifying the name to avoid the search blackout.10 Some participants changed their display name to variations of the name and “whistleblower.”
An organized effort to increase campaign participation and further seed the name on social media began in earnest on December 12. In a 4chan thread on December 12 that used the name in its title, a campaign operator laid out the strategy to attract attention: “We need to take up the responsibility of making sure everyone knows his name, no matter how hard the media tries to suppress it. i.e if you're talking about the impeachment with friends or family, casually bring up his name.”11 The post encouraged participants to use “C’s” name in hashtags along with other trending hashtags on Twitter to “let everyone you know be aware” of the name and “why they should care.” As a result of tactical adjustments like this, it remains easy to find tweets that explicitly accuse "C" of being the whistleblower.
- 1Kevin Reed, “Facebook and Remove Posts Naming CIA Impeachment Whistleblower” World Socialist Web Site, November 11, 2019, https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2019/11/11/face-n11.html.
- 2Justin Wise, “YouTube Removes Video of Rand Paul Reading Alleged Whistleblower’s Name on Senate Floor,” Text, The Hill, February 13, 2020, https://thehill.com/homenews/senate/482897-youtube-removes-video-of-rand-paul-reading-alleged-whistleblowers-name-on.
- 3Madison Dibble, “‘Dystopian Nightmare’: Journalist Complains YouTube Blocked Video about Alleged Whistleblower Eric Ciaramella,” The Washington Examiner, November 10, 2019, https://www.washingtonexaminer.com/news/dystopian-nightmare-journalist-complains-youtube-blocked-video-about-alleged-whistleblower-eric-ciaramella.
- 4Lauren Feiner, “Reddit Will Allow the Alleged Ukraine Whistleblower’s Name to Surface, Diverging from Facebook and YouTube,” CNBC, November 12, 2019, https://www.cnbc.com/2019/11/12/reddit-allows-alleged-whistleblowers-name-to-surface.html.
- 5T.D. Adler, “Wikipedia Admins Censor Name of Alleged Ukraine ‘Whistleblower,’” Breitbart, November 10, 2019, https://www.breitbart.com/tech/2019/11/10/wikipedia-admins-censor-name-of-alleged-ukraine-whistleblower/.
- 6“Trump–Ukraine Scandal,” Wikipedia, August 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trump%E2%80%93Ukraine_scandal#Whistleblower_rules_and_hearsay.
- 7Kaplan, “How a Total Fabrication Connecting George Soros’ Son to the Whistleblower Went from the Underbelly of the Internet to Rep. Steve King.”
- 8 Beatrice Dupuy, “Photos Do Not Show Whistleblower with Warren, Pelosi and Others,” AP NEWS, November 14, 2019, https://apnews.com/afs:Content:8150150005.
- 9Isabella Fertel, “Viral Posts Misidentify Soros’ Son as the Whistleblower,” FactCheck.Org (blog), November 15, 2019, https://www.factcheck.org/2019/11/viral-posts-misidentify-soros-son-as-the-whistleblower/.
- 10Sheera Frenkel, “Whistle-Blower’s Purported Name Keeps Evading Facebook and YouTube Defenses,” The New York Times, November 14, 2019, https://www.nytimes.com/2019/11/14/technology/whistleblower-name-facebook-youtube.html; Ryan Broderick, “Right-Wing Publishers Have Found A Way To Post The Supposed Trump Whistleblower’s Name To Facebook,” BuzzFeed News, December 27, 2019, https://www.buzzfeednews.com/article/ryanhatesthis/trump-whistleblower-name-facebook.
- 11Anonymous, “/pol/ - Politically Incorrect » Thread #236024725,” 4chan, December 12, 2019, accessed via 4plebs, https://archive.4plebs.org/pol/thread/236024725/.
Cite this case study
Joan Donovan and Brian Friedberg, "Targeted Harassment: The Ukraine Whistleblower," The Media Manipulation Case Book, July 7, 2021, https://casebook-static.pages.dev/case-studies/targeted-harassment-ukraine-whistleblower.


![On November 19, Republican congressman Steve King shared an Alexander Soros misidentification collage, commenting, “Adam Schiff [Democratic congressman] said, I do not know the identity of the whistleblower. @RepAdamSchiff here are four strong clues.” Credit: Screenshot by @IAStartingLine on Twitter.](/sites/default/files/styles/large_image_small_/public/large-image/2020-10/Screen%20Shot%202020-10-19%20at%207.02.06%20PM.png)